

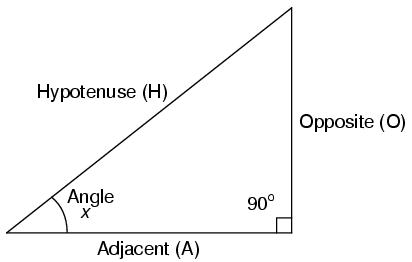
A right triangle is defined as having one angle precisely equal to 90o (a right angle).

H is the Hypotenuse, always being opposite the right angle. Relative to angle x, O is the Opposite and A is the Adjacent.
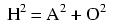
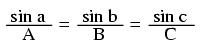
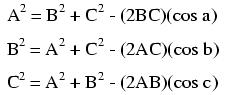
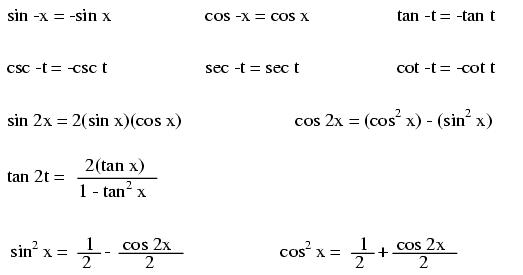
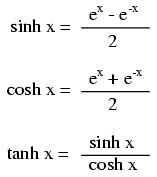
Note: all angles (x) must be expressed in units of radians for these hyperbolic functions. There are 2π radians in a circle (360o).


